The router will respond with the MAC address of its interface the one which is connected to the same network as the. The transport layer guarantees that no duplicate data arrive at the destination.
Solved Which Destination Address Is Used In An Arp Request Chegg Com
Similarly it allows the receiver to identify and discard duplicate segments.
. An ARP request will be sent by the source and will be responded to by the router. Here is a short sample taken from the start of an rlogin from host rtsg to host csam. Sender is not allowd to communicate with destination.
Switch will forward the frame out all interfaces except the incoming interface. In the network layer DHCP messages are always broadcast. The default is the broadcast address ffffffffffff.
It is used to find layer 3 address from layer 2 address like DLCI in frame relay. When sending a packet to a remote destination a host will need to send the packet to a gateway on the local subnet. When using inverse ARP we know the DLCI or remote router but dont know its IP address.
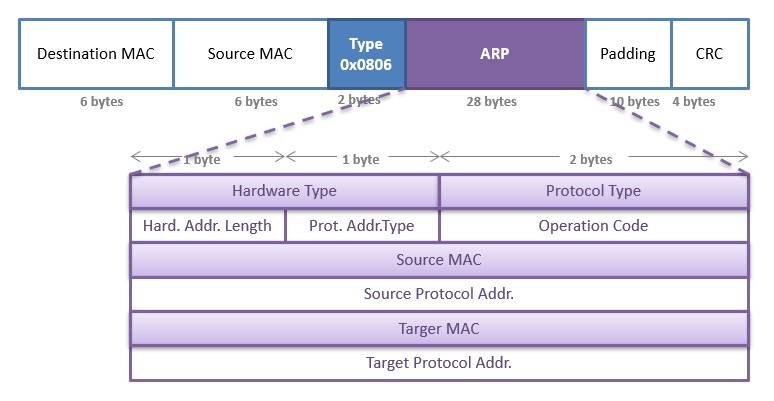
The ARP Request is an ARP payload carried within the appropriate L2 frame for the medium in use. Open Shortest Path First OSPF is a link-state routing protocol that is used to find the best path between the source and the destination router using its own Shortest Path First. The network host IP interface binds the gateway address to the MAC address of the physical gateway by broadcasting IP datagrams and caching the MAC address of the reply from the gateway in an ARP table.
Because the gateway will be the Layer 2 destination for the frame on this LAN segment the destination MAC address must be the address of. The used MAC address for the reply can be specified. Which destination address is used in an ARP request frame.
The purpose of an ARP request is to find the MAC address of the destination host on an Ethernet LAN. --destaddr or -T Send the packets to Ethernet MAC address This sets the 48-bit destination address in the Ethernet frame header. Each device on the segment will receive the packet but.
When a frame is sent to a device not on the local network the gateways MAC address is used in the frame header. It dynamically maps local DHCP or remote IP addresses when you configure frame relay. A Destination MAC address a Source MAC address and an EtherType.
The answer is that it will do it by following the Address resolution Protocol. Flow control is used to prevent the sender from overwhelming the receiver. A table is created by the network administrator in the gateway-router that is used to find out the MAC address to the corresponding IP address.
The majority of the time this will be Ethernet which will also be the L2 medium we will be looking at in our examples. The gateway address must be configured on each host. In the data link layer also DHCP messages are broadcast.
The format is intended to be self explanatory. The command-line options of the ping utility and its output vary between the numerous. Now lets see what happens when DHCP clients request a DHCP server an IP address.
If this target sees an ARP request it will automatically reply with an ARP reply. In order to find out the MAC address of host B host A sends an ARP request listing the host Bs IP address as the destination IP address and the MAC address of FFFFFFFFFFFF Ethernet broadcast. The ARP request packet is then encapsulated in an Ethernet frame with the MAC address of Host A as the source address and a broadcast FFFFFFFFFFFF as the destination address.
The ARP request packet is then encapsulated in an Ethernet frame with the MAC address of Host A as the source address and a broadcast FFFFFFFFFFFF as the destination address. Arp who-has csam tell rtsg arp reply csam is-at CSAM The first line says that rtsg sent an ARP packet asking for the Ethernet address of internet host. Destination host unknown is sent from destination network router.
A frame is encapsulated with source and destination MAC addresses. This is the first message in the DORA process. The protocol must be specified as ARP.
ARPRARP output shows the type of request and its arguments. Note that the ARP Reply has the Opcodef filled as 2 which is used to identify it as a ARP Reply. Lets see what messages are exchanged between them in the process.
Now lets break this down a little bit to understand how the MAC address table is built and used by an Ethernet switch to help traffic move along the path to its destination. When the computer with the IP Address 1921680122 receives the ARP Request it must prepare an ARP Reply and send back to the computer who sent the ARP Request. When using Nmap on a local network ARP protocol is applied by default for being faster and more reliable.
If the switches at the layer-2 dont follow any routing table then how they will learn the MAC address unique address of a machine like 3C-95-09-9C-21-G2 of the next hop. Since the ARP request is a broadcast it reaches all the nodes in the Subnet A which includes the e0 interface of the router but does not reach Host D. Nping allows to generate packet under many protocols as it official website describes it can also be used for ARP poisoning Denial of.
If the receiver is overloaded with too. Sequence numbers are used to identify the lost packets. When the ARP message is not an ARP request or when the ARP request isnt for an IP address on an Ethernet network it is ignored by this target CONTINUE.
Layer 2 broadcast means that frame will be sent to all hosts in the same layer 2 broadcast domain which includes the ether0 interface of the router but does not reach Host D because router by default. A MAC address table sometimes called a Content Addressable Memory CAM table is used on Ethernet switches to determine where to forward traffic on a LAN. The Ethernet header will include three fields.
It will send an ARP request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address. ARP Address Resolution Protocol is a low level protocol working at Link layer level of the Internet Model or Internet protocol suite. MAC Address Tables.
ARP Reply will be a unicast to save Network Resources. Reverse ARP RARP - It is a networking protocol used by the client system in a local area network LAN to request its IPv4 address from the ARP gateway router table. From the above introduction about both the layer switches an interesting question arises in our mind.
Most operating systems will also respond if the ARP request is sent to their MAC address or to a multicast address that they are listening on. The source device will not know the MAC address of the remote host. The program reports errors packet loss and a statistical summary of the results typically including the minimum maximum the mean round-trip times and standard deviation of the mean.
--arpsha or -u Use. Meaning that the host is unknown. The ARP process sends a Layer 2 broadcast to all.
Communication with destination network is administratively prohibited. OSPF is developed by Internet Engineering Task Force IETF as one of the Interior Gateway Protocol IGP ie the protocol which aims at moving the packet within a large autonomous. 0000 255255255255 FFFFFFFFFFFF AAAAAAAAAAAA the physical address of the destination host Answers Explanation Hints.
Pinging involves sending an ICMP echo request to the target host and waiting for an ICMP echo reply.

Arp Address Resolution Protocol Explained

0 Comments